PTA上C语言学习,细节方面有收获的地方与PAT乙级刷题心得。
PTA PTA上没有一下子想到方法的题
下面附上代码:
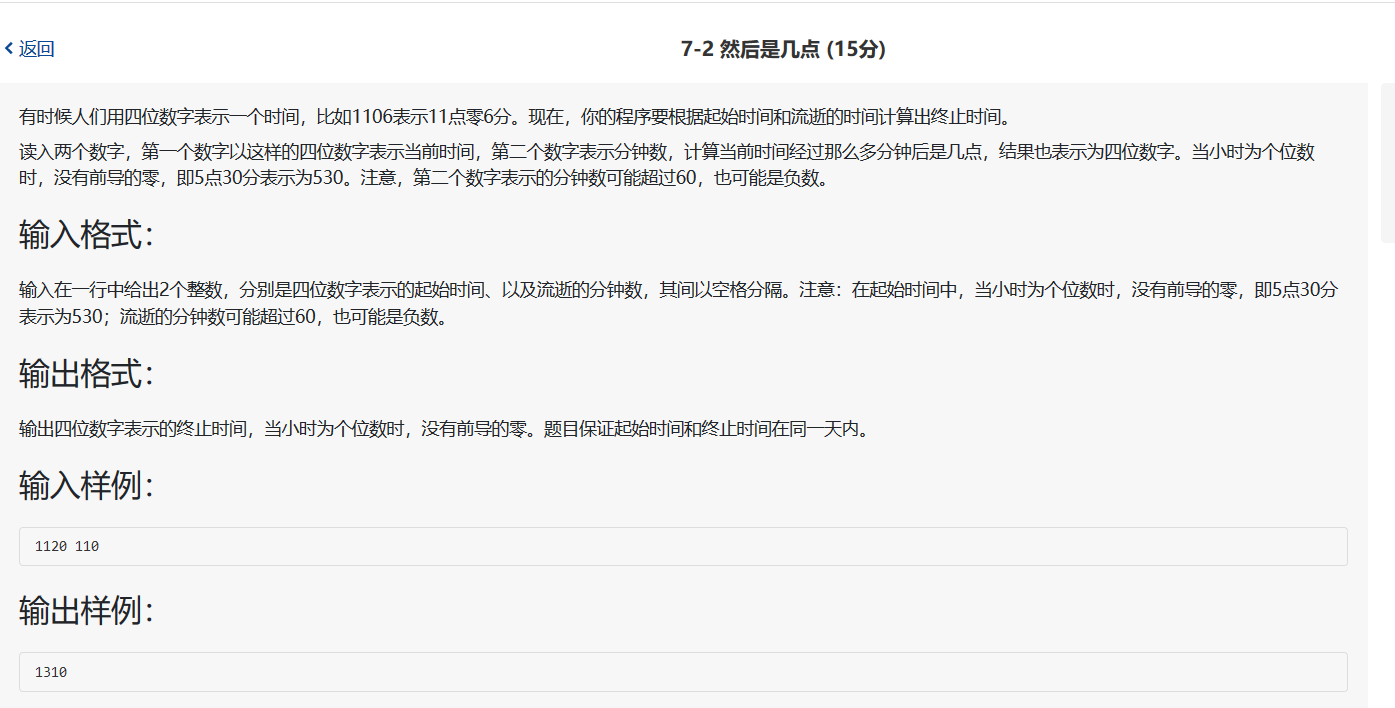
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int m = 0 , n = 0 , hours = 0 , minute = 0 , end_time = 0 ; scanf ("%d %d" , &m, &n); hours = m/100 , minute = m%100 ; hours += n/60 , minute += n-(n/60 )*60 ; if (minute >= 60 ) hours += 1 , minute -= 60 ; if (minute < 0 ) hours -=1 , minute += 60 ; end_time = hours*100 + minute; printf ("%d" , end_time); return 0 ; }
PTA中做一道题,注意细节心得
下面附上代码:
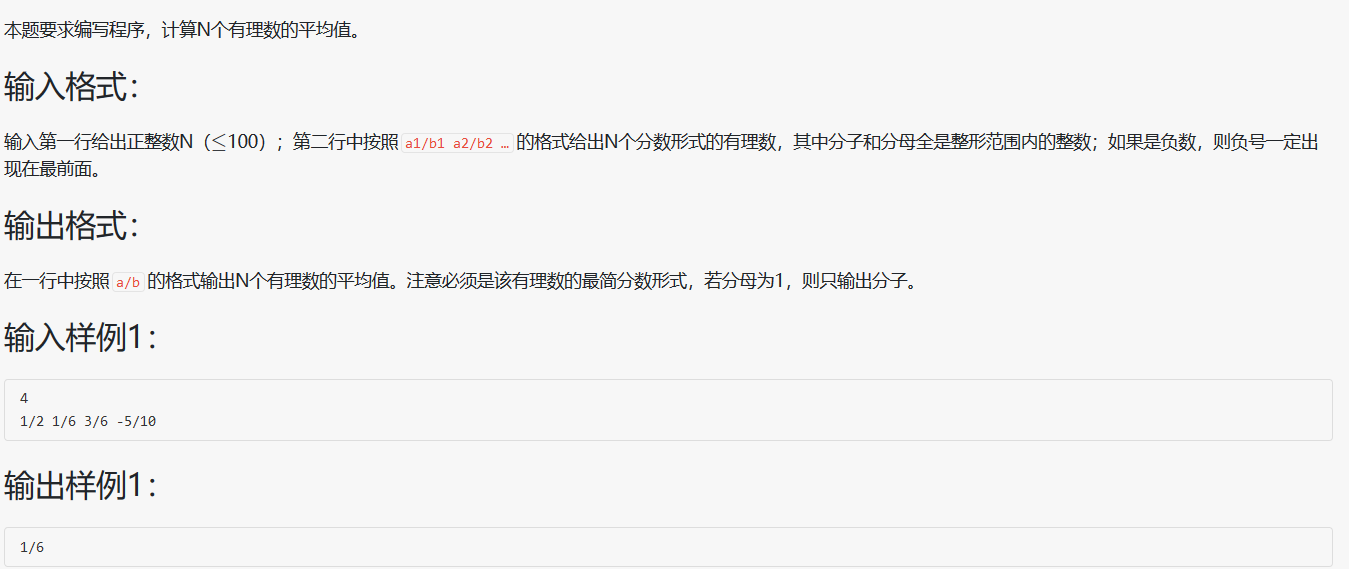
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <stdio.h> int gcd (int a, int b) int c = 0 ; while (b) { c = a%b; a = b; b = c; } return a; } int main (void ) int N = 0 , temp = 0 , g = 0 , temp_N = 0 ; int a = 0 , b = 0 , min = 0 , sum_a = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &N); temp_N = N; for (; N; N--) { scanf ("%d/%d" , &a, &b); if (min ) { temp = min ; min = (min *b)/gcd(min , b); sum_a *= (min /temp), sum_a += (min /b)*a; } else min = b, sum_a += a; g = gcd(sum_a, min ); sum_a /= g, min /= g; } N = temp_N; min *= N; g = gcd(sum_a, min ); sum_a /= g, min /= g; if (min > 1 ) printf ("%d/%d" , sum_a, min ); else printf ("%d" , sum_a); return 0 ; }
删除子字符串的一道好题 (方法可以掌握)
下面题解:
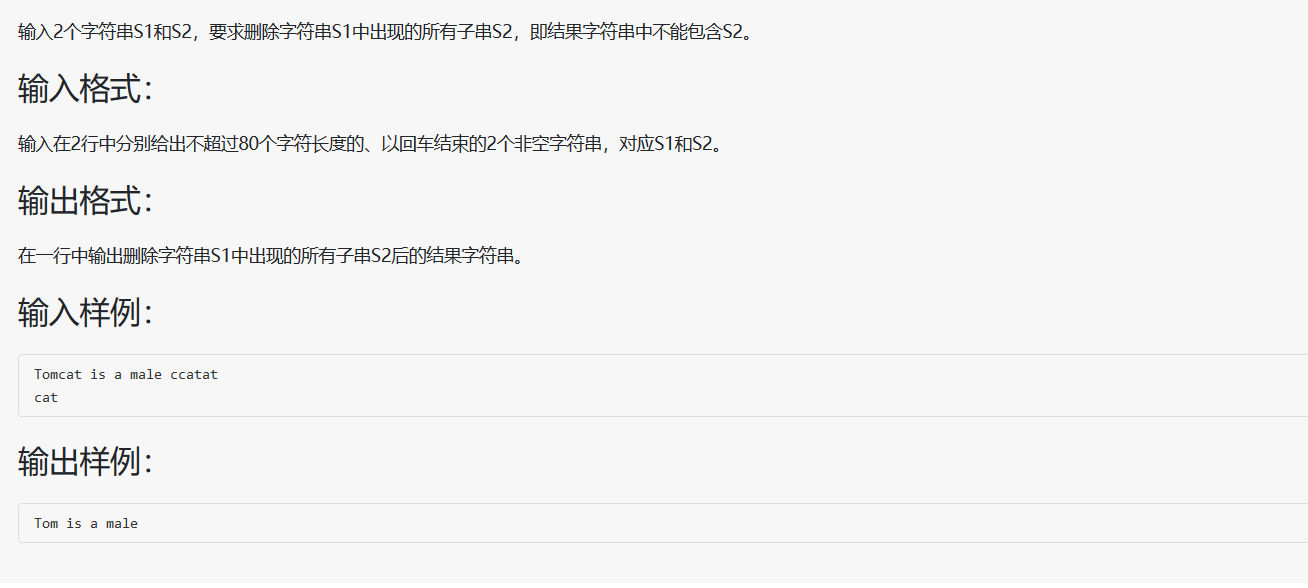
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main (void ) char *p = NULL ; char s[81 ] = {0 }, t[80 ] = {0 }; gets(s), gets(t); while (p = strstr (s, t)) { *p = '\0' ; strcat (s, p+strlen (t)); } puts (s); return 0 ; }
一道题因为没有注意, 阶乘并不是 a *= a+2, 花了很多时间找错
下面代码:
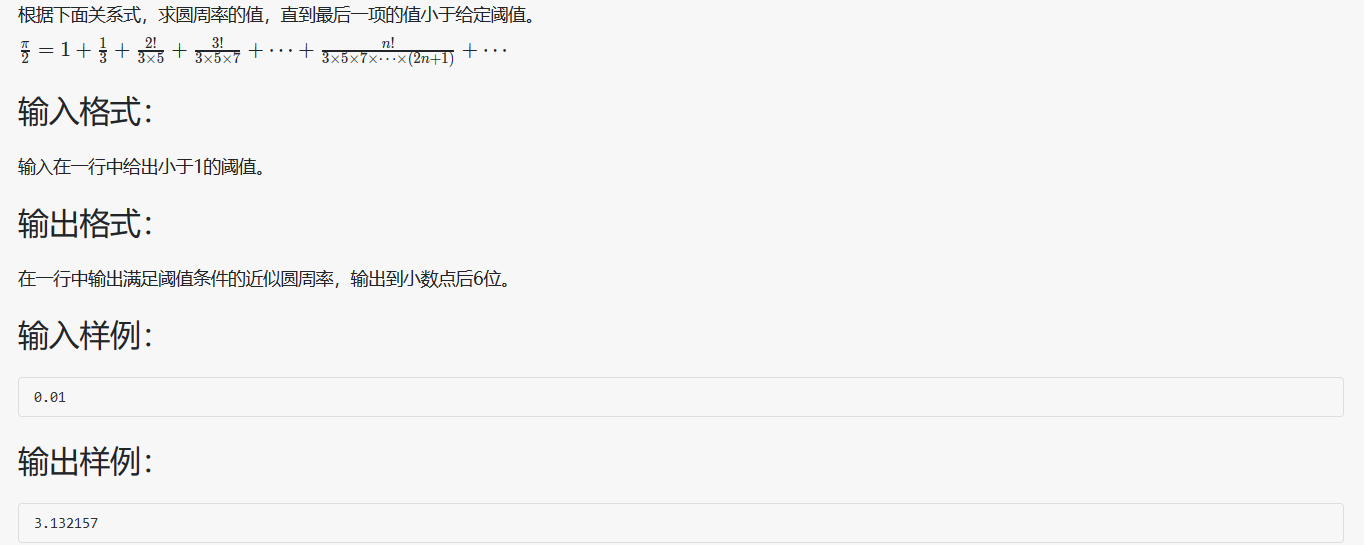
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) double i = 2 ; double sum = 2 , x = 0 , a = 1 , b = 3 ; scanf ("%lf" , &x); for ( ; 2 *a/b >= x; a *= i, b *= (2 *(i++) + 1 )) sum += 2 *a/b; sum += 2 *a/b printf ("%.6lf" , sum); return 0 ; }
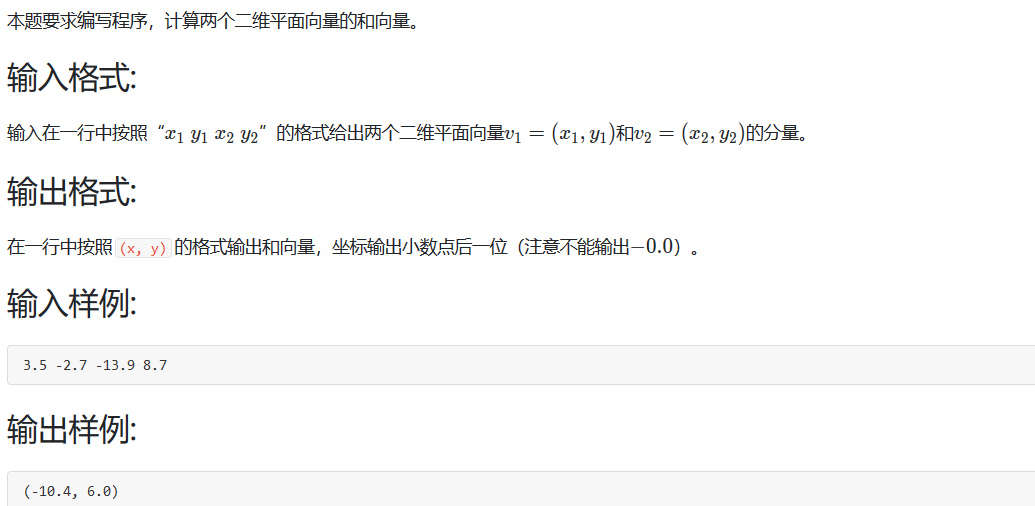
平面向量加法
可以看到题目就是简单的加法, 但是这里考了个知识点, 正是我不知道的. 所以改了好几次才通过.
因为在C语言整数都是不管四舍五入的, 直接舍弃小数部分. 到了浮点数我默认以为保留几位小数时,也是直接舍弃多余小数部分, 但其实是四舍五入.
下面题解.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) double a = 0 , b = 0 , c = 0 , d = 0 ; double m = 0 , n = 0 ; scanf ("%lf %lf %lf %lf" , &a, &b, &c, &d); m = a+c, n = b+d; if (m > -0.05 && m < 0 ) m = 0 ; if (n > -0.05 && n < 0 ) n = 0 ; printf ("(%.1lf, %.1lf)" , m, n); return 0 ; }
查找书籍 gets()后不产生回车。只是把最后输入的回车转化为 ‘\0’ 。
PAT 520 钻石争霸赛 其中2道很简单的题,但做的时候都有一个测试点怎么也过不了。。。当时真想不明白,比赛结束后来看了很久还是没发现错误,很想知道到测试点是什么,但这是不可能的。。。后面一度认为题目对C语言的问题,hh。其实不是,今天找到了问题,2个题还犯了同一种错误,记录一下。
1.首先是简单的求平均成绩,问题就出现在如果成一个人的成绩是0的话,总成绩为0,但人数增加了一个啊。而我们一直使用的分数来确定是否有人存在。。。找这个错误真不容易诶。
代码警示错误。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int N = 0 , sum_0 = 0 , sum_1 = 0 ; int n = 0 , score = 0 ; int count_1 = 0 , count_2 = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &N); while (N--) { scanf ("%d %d" , &n, &score); if (n) sum_1 += score, count_1++; else sum_0 += score, count_2++; } printf ("%.1lf" , (double )(sum_1+sum_0)/(count_1+count_2)); if (count_1) printf (" %.1lf" , (double )sum_1/count_1); else printf (" X" ); if (count_2) printf (" %.1lf" , (double )sum_0/count_2); else printf (" X" ); return 0 ; }
2.下面这个题犯了差不多的错。可以看到,就是倒序输出数字,可以很多方法。我使用的将每位数字先分离出来存入一个数组,在倒序输出。 但这里有一个0的情况,如果数字为0,那分离数字的结果就是什么也没有即什么也不输出。。
这里其实直接转化为字符串输出就好了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int a = 0 , b = 0 , i = 0 ; char ch[13 ] = {0 }; scanf ("%d %d" , &a, &b); sprintf (ch, "%d" , a += b); for (; ch[i]; printf ("%c\n" , ch[i++])); return 0 ; }
总结:2个题遇到同种类型的错误,折磨了我很久,但对自己进行补漏了。注意0的情况很重要。
3.这个题注意,题目只说了输入的第一个数字没超过1000位,第二个未知的,有点小坑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> int main (void ) char a[10001 ] = {0 }, b[2001 ] = {0 }; int sum = 0 , lenth1 = 0 , lenth2 = 0 ; int i = 0 ; gets(a); lenth1 = strlen (a); gets(b); while (*b != '-' ) { lenth2 = strlen (b); if (lenth1 != lenth2) printf ("No\n" ); else { for (i = 0 ; i < lenth1; i++) sum += abs (a[i]-b[i]); if (sum <= 1 ) printf ("Yes\n" ); else printf ("No\n" ); } sum = 0 , gets(b); } return 0 ; }
4.处理好每次赢输之间的变换。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main (void ) char s[10 ] = {0 }, flag = 0 ; int N = 0 , a[10 ] = {0 }, i = 0 , j = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &N); for (i = 0 ; i < N; i++) scanf ("%d" , &a[i]); getchar(); while (1 ) { if (!flag) { for (i = 0 ; i < a[j%N]; i++) { gets(s); if (*s == 'E' ) return 0 ; if (*s == 'C' ) printf ("Bu\n" ); else if (*s == 'J' ) printf ("ChuiZi\n" ); else printf ("JianDao\n" ); flag = 1 ; } } else { gets(s); if (*s == 'E' ) return 0 ; if (*s == 'C' ) printf ("JianDao\n" ); else if (*s == 'J' ) printf ("Bu\n" ); else printf ("ChuiZi\n" ); flag = 0 , j++; } } return 0 ; }
PAT乙级 我要通过
题目的难点也就是条件三,如果没有理解到位,总是会有条件过不了。。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <stdio.h> int judge (char *a) int flag = 0 , other = 0 ; int p = 0 , t = 0 , i = 0 ; int q = 0 , z = 0 , h = 0 ; while (a[i]) { if (a[i] == 'A' ) if (flag == 0 ) q++; else if (flag == 1 ) z++; else h++; else if (a[i] == 'P' ) p++, flag = 1 ; else if (a[i] == 'T' ) t++, flag = 2 ; else other++; if (t == 1 && p == 0 ) return 0 ; i++; } if (!other && z && q*z == h && p == 1 && t == 1 ) return 1 ; return 0 ; } int main (void ) int n = 0 ; char a[101 ] = {0 }; scanf ("%d" , &n); getchar(); while (n--) { gets(a); if (judge(a)) printf ("YES\n" ); else printf ("NO\n" ); } return 0 ; }
1007 素数对猜想 主要记录一下素数的优化技巧,这个题只是用普通的方法判断会在最后一个测试点超时。
偶数除2之外都不是素数,所以在判断那些是素数时,可以把2单独处理,其他的每次加2,只看奇数。 在素数判断时,先对所要判断的数开平方,时间复杂度大大降低。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int prime_number (int a) int i = 0 , temp = (int )sqrt ((double )a); for (i = 2 ; i <= temp; i++) if (a%i == 0 ) return 0 ; return 1 ; } int main (void ) int i = 0 , N = 0 , count = 0 , temp = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &N); temp = 2 ; for (i = 3 ; i <= N; i += 2 ) if (prime_number(i)) count += i-temp == 2 ? 1 :0 , temp = i; printf ("%d" , count); return 0 ; }
1008 数组元素循环右移问题 本以为秒答的题,有个测试点,卡半天。我发现写程序什么错误都会犯。。
这里还是先总结一下,关于数组循环移动输出的问题:假设数组:a,长度:len
循环左移n位:a[n+i%len] 循环右移n位:与左移原理一样,只不起始点用总长度减一下:a[(len-(n%len)+i)%n] 题目:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int n = 0 , a[200 ] = {0 }, span = 0 , i = 0 ; scanf ("%d %d" , &n, &span); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) scanf ("%d" , a+i); printf ("%d" , a[(n-span%n)%n]); for (i = 1 ; i < n; i++) printf (" %d" , a[(n-span%n+i)%n]); return 0 ; }
总结:我都不知道我怎么找这么一个错误的。
1010 一元多项式求导 题目感觉简单,但是好坑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int i = 0 , j = 0 ; int pre = 0 , cur = 0 ; scanf ("%d %d" , &pre, &cur); if (!cur) printf ("0 0" ); else { printf ("%d %d" , pre*cur, cur-1 ); while (scanf ("%d %d" , &pre, &cur) != EOF) if (cur) printf (" %d %d" , pre*cur, cur-1 ); } return 0 ; }
总结:对输入的如何限定停止。
1014 福尔摩斯的约会 感觉题目很多都不说明,自己在哪里猜有没有限制条件,结果都有。。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) char s[4 ][61 ] = {0 }, i = 0 , j = 0 , count = 0 ; char *day[8 ] = {" " , "MON" , "TUE" , "WED" , "THU" , "FRI" , "SAT" , "SUN" }; while (i < 4 ) gets(s[i]), i++; for (i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i += 2 ) { for (j = 0 ; s[i][j] && s[i+1 ][j]; j++) { if (i == 0 && s[i][j] == s[i+1 ][j]) { if (count == 0 && s[i][j] >= 65 && s[i][j] <= 71 ) { printf ("%s " , day[s[i][j]-64 ]); count++; } else if (count == 1 && (s[i][j] >= 'A' && s[i][j] <= 'N' || s[i][j] >= 48 && s[i][j] <= 57 )) { printf ("%02d:" , s[i][j] >= 48 && s[i][j] <= 57 ? s[i][j]-48 : s[i][j]-55 ); break ; } } else if (i > 1 && s[i][j] == s[i+1 ][j] && (s[i][j] >= 65 && s[i][j] <= 90 || s[i][j] >= 97 && s[i][j] <= 122 )) { printf ("%02d\n" , j); break ; } } } return 0 ; }
其中有个平时没注意过的地方,i > 1 && s[i][j] == s[i+1][j] && (s[i][j] >= 65 && s[i][j] <= 90 || s[i][j] >= 97 && s[i][j] <= 122)),对于这判断式,后面有 || 就一定要加上括号,不然它满足了,判断式就直接成立了。。。
总结:注意题目隐含条件。
1015 德才论 这道题自己开始做起来还是挺难的,先分类后冒泡排序,但一般会有测试点超过,果然。后面尝试使用C语言的qsort(),成功了,从这道题,对qsort()使用变得深入很多。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef struct { int id; int d; int c; }Stu; int low = 0 , high = 0 ;int check (const Stu *a) if (a->d >= high && a->c >= high) return 1 ; else if (a->d >= high && a->c >= low) return 2 ; else if (a->d >= low && a->c >= low && a->d >= a->c) return 3 ; else if (a->d >= low && a->c >= low) return 4 ; else return 5 ; } int cmp (const void *a, const void *b) Stu *a1 = (Stu *)a, *b1 = (Stu *)b; int sum = a1->c+a1->d, sum1 = b1->c+b1->d; if (check(a1) == check(b1)) { if (sum == sum1) { if (b1->d == a1->d) return a1->id - b1->id; else return b1->d - a1->d; } else return sum1-sum; } else return check(a1)-check(b1); } int main (void ) int n = 0 , count = 0 , i = 0 , j = 0 ; scanf ("%d %d %d" , &n, &low, &high); Stu *stu = (Stu *)malloc (sizeof (Stu)*n); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { scanf ("%d %d %d" , &stu[i].id, &stu[i].d, &stu[i].c); count += stu[i].d >= low && stu[i].c >= low ? 1 :0 ; } qsort(stu, n, sizeof (Stu), cmp); printf ("%d\n" , count); for (i = 0 ; i < count; i++) printf ("%d %d %d\n" , stu[i].id, stu[i].d, stu[i].c); return 0 ; }
总结:这道题主要二点,一:想到先划分类,二:如何使用上qsort()函数。
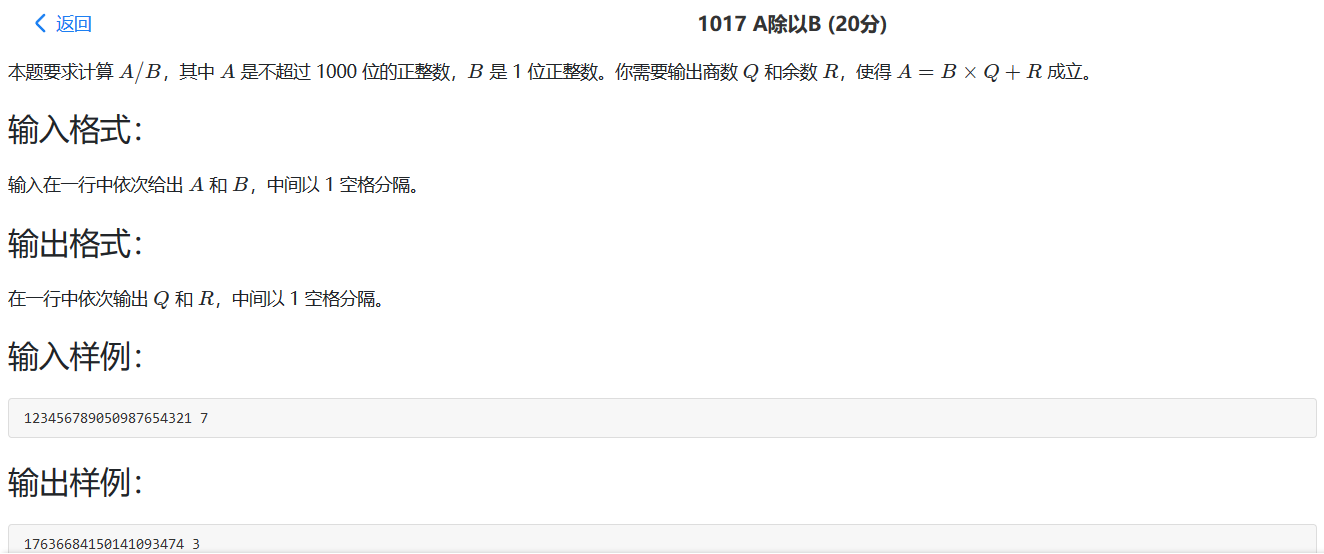
1017 A除以B 这个题使用C语言来写就是一个大数除法,使用平常手算除法的思想,从开始除到最后。但是这个题使用python来做的话就只是函数的调用。
C语言:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main (void ) char s[1001 ] = {0 }; int n = 0 , temp = 0 , ans = 0 , len = 0 , i = 0 ; scanf ("%s %d" , s, &n); len = strlen (s); ans = (s[0 ]-48 )/n; if (len == 1 || ans) printf ("%d" , ans); temp = (s[0 ]-48 )%n; for (i = 1 ; i < len; i++) { ans = (temp*10 +s[i]-48 )/n; printf ("%d" , ans); temp = (temp*10 +s[i]-48 )%n; } printf (" %d" , temp); return 0 ; }
python:
1 2 3 n = input().split() q, r = divmod(int(n[0 ]), int(n[1 ])) print (str(q)+' ' +str(r))
总结:对大数除法使用手算除法的第一次简单应用。
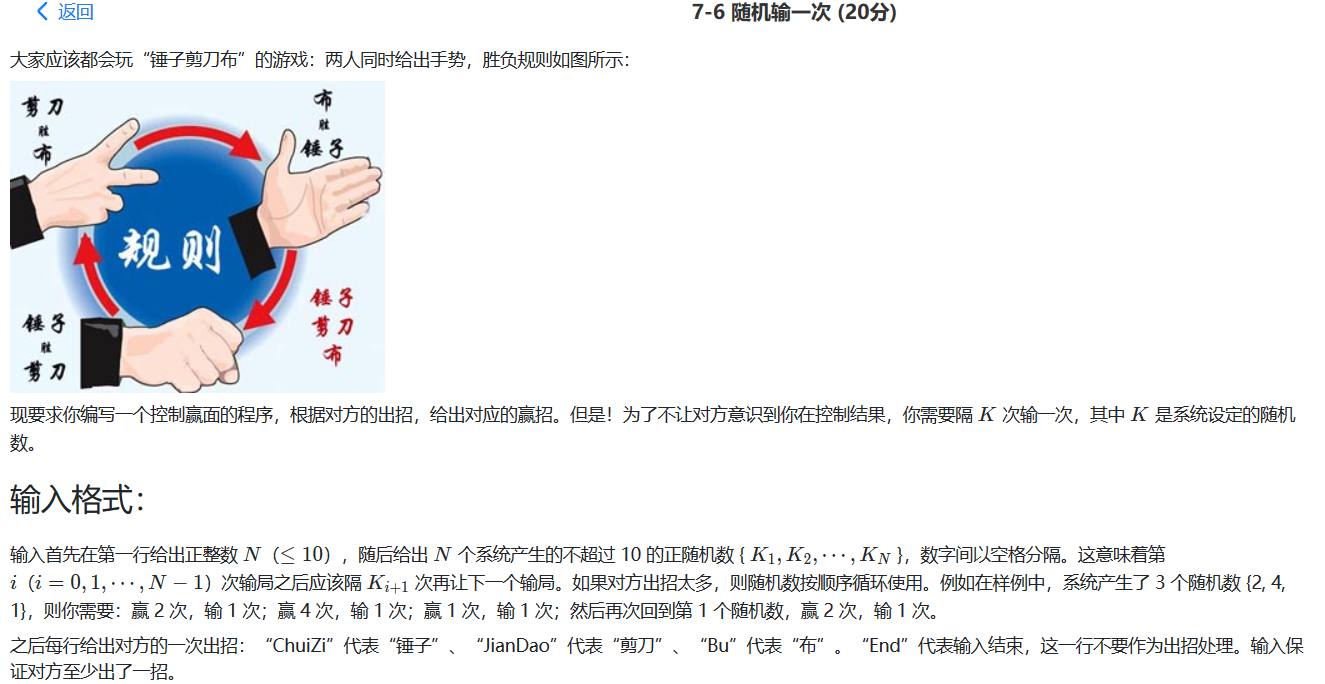
1018 锤子剪刀布 我发现只要题目写起来比自己预想的代码量大,我就会焦躁,感觉题目不会有那么麻烦,想哪里写的罗嗦了 ,怎么这个都不会之类。导致最后就是更不想做题了。这个题就是个例子,开始预想的很简单,代码也少,但这个题确实判断有点繁琐,尽管有简单的写法,也在自己能力之外吧。
麻烦的地方就是图中标注的地方。自己用的好像是一个类似哈希表的东西,因为没学过。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int n = 0 , i = 0 , max = 0 , max1 = 0 ; char ch1 = 0 , ch2 = 0 , s[4 ] = {'B' , 'C' , 'J' , 0 }; int a = 0 , b = 0 , c = 0 , map [127 ] = {0 }, map1[127 ] = {0 }; scanf ("%d" , &n); getchar(); while (i++ < n) { scanf ("%c %c" , &ch1, &ch2); getchar(); if (ch1 == 'C' && ch2 == 'J' ) a++, map ['C' ]++; else if (ch1 == 'C' && ch2 == 'B' ) c++, map1['B' ]++; else if (ch1 == 'B' && ch2 == 'J' ) c++, map1['J' ]++; else if (ch1 == 'B' && ch2 == 'C' ) a++, map ['B' ]++; else if (ch1 == 'J' && ch2 == 'B' ) a++, map ['J' ]++; else if (ch1 == 'J' && ch2 == 'C' ) c++, map1['C' ]++; else b++; } printf ("%d %d %d\n" , a, b, c); printf ("%d %d %d\n" , c, b, a); for (i = 0 ; s[i]; i++) { max = map [s[i]] > max ? map [s[i]]:max ; max1 = map1[s[i]] > max1 ? map1[s[i]]:max1; } for (i = 0 ; s[i]; i++) if (map [s[i]] >= max ) { printf ("%c " , s[i]); break ; } for (i = 0 ; s[i]; i++) if (map1[s[i]] >= max1) { printf ("%c" , s[i]); break ; } return 0 ; }
总结:做题就算有简单解法,把当下麻烦的解法写完再说。
1019 数字黑洞 感觉PTA乙级题的坑好多。。不注意的话又是大量时间找错。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int cmp1 (const void *a, const void *b) char *p = (char *)a, *q = (char *)b; return *q-*p; } int cmp2 (const void *a, const void *b) char *p = (char *)a, *q = (char *)b; return *p-*q; } int re (char *s, int (*cmp)(const void *, const void *)) int n = 0 ; qsort(s, strlen (s), sizeof (char ), cmp); sscanf (s, "%d" , &n); return n; } int main (void ) char s[5 ] = {0 }; int n = 0 , n_re = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &n), sprintf (s, "%04d" , n); n = re(s, cmp1), n_re = re(s, cmp2); while (n-n_re != 0 && n-n_re != 6174 ) { printf ("%04d - %04d = %04d\n" , n, n_re, n-n_re); sprintf (s, "%04d" , n-n_re); n = re(s, cmp1), n_re = re(s, cmp2); } printf ("%04d - %04d = %04d\n" , n, n_re, n-n_re); return 0 ; }
总结:注意逆序一个数字时他前面的0。
1020 月饼 为什么做PTA的题总是很气。。这个题第一个测试点磨了我2个小时???其实也不怪题,只是很多题都考到了我没注意过的小细节。。那也是收获。
我卡了2小时的一个测试点,错误:qsort的比较函数的返回值是int,这次题目的数据是浮点数,所以如果当两个浮点数相差小于1的时候,返回的值为变成int型的0,那就不会发生排序了。即我用的return q->price_single - p->price_single;,当他们2个数相差小于1就返回0,导致结果是不排序。这里正确的写法应该是return q->price_single > p->price_single;,以后都写大于小于了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <stdio.h> typedef struct { double ku, price_all, price_single; }Cake; int cmp (const Cake *a, const Cake *b) return b->price_single > a->price_single; } int main (void ) Cake cake[1000 ]; double ans = 0 ; int n = 0 , demand = 0 , i = 0 ; scanf ("%d %d" , &n, &demand); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) scanf ("%lf" , &cake[i].ku); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { scanf ("%lf" , &cake[i].price_all); cake[i].price_single = cake[i].price_all/cake[i].ku; } qsort(cake, n, sizeof (Cake), cmp); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (cake[i].ku <= demand) { ans += cake[i].price_all; demand -= cake[i].ku; } else { ans += cake[i].price_single*demand; break ; } } printf ("%.2lf" , ans); return 0 ; }
总结:1.我感觉这个的难点是能不能想到构造结构体。2.对数据不敏感,一直被坑在qsort的比较函数。
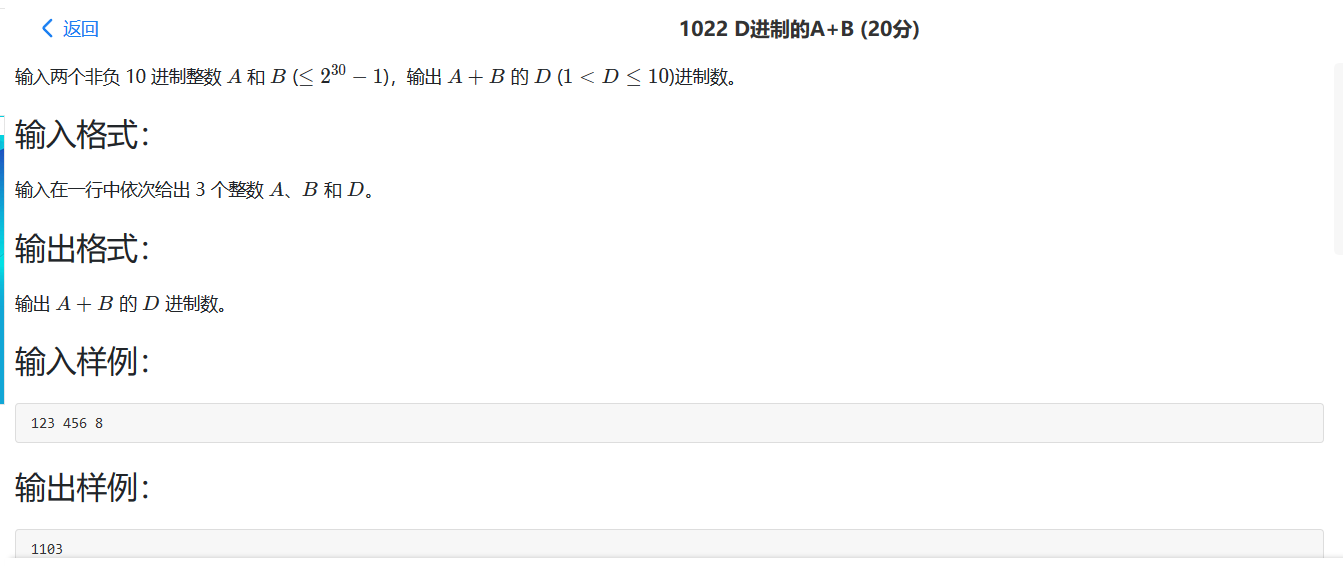
1022 D进制的A+B 就是让写一个10进制数转任意指定的进制数,以前接触过,这里写2种方法。递归与非递归。
注释了的为递归写法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <stdio.h> char s[] = "0123456789ABCDEF" ;int main (void ) int a = 0 , b = 0 , d = 0 , c = 0 ; char s1[1000 ] = {0 }, i = 0 ; scanf ("%d %d %d" , &a, &b, &d); for (c = a+b; c; s1[i++] = c%d, c /= d); if (!i) printf ("0" ); while (--i >= 0 ) printf ("%c" , s[s1[i]]); return 0 ; }
1023 组个最小数 换个算法, 做对了。但一直想不通之前的算法为什么有2个测试点过不了,折磨了我差不多一天。。。找错真的好难,吐槽一下PAT为什么不给出测试点。
错误:我用字符表示整数时是要ASCII-48,但我只考虑到了0-9的情况,当数字大于9后就不能直接减去48了,并且会被当作2个字符处理。
这里先给出简单的代码:就是先找到第一个非0数先输出,再将其个数减一,最后输出所有。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int a[10 ], i = 0 ; for (i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) scanf ("%d" , a+i); for (i = 1 ; i < 10 ; i++) if (a[i]) { printf ("%d" , i); a[i]--; break ; } for (i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) while (a[i]) { printf ("%d" , i); a[i]--; } return 0 ; }
折磨我的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) char s[150 ] = {0 }, i = 0 , j = 0 , ch = 0 ; while ((ch = getchar()) != 10 ) { if (ch != 32 ) { ch -= 48 ; while (ch--) s[i++] = j+48 ; j++; } } if (s[0 ] == 48 ) { i = 1 ; while (s[i++] == 48 ); ch = s[i-1 ]; s[i-1 ] = s[0 ]; s[0 ] = ch; } puts (s); return 0 ; } int main (void ) int ch = 0 ; char s[150 ] = {0 }, i = 0 , j = 0 ; while ((scanf ("%d" , &ch))) { if (j == 10 ) break ; while (ch--) s[i++] = j+48 ; j++; } if (s[0 ] == 48 ) { i = 1 ; while (s[i++] == 48 ); ch = s[i-1 ]; s[i-1 ] = s[0 ]; s[0 ] = ch; } puts (s); return 0 ; }
总结:找到错后,舒服了。
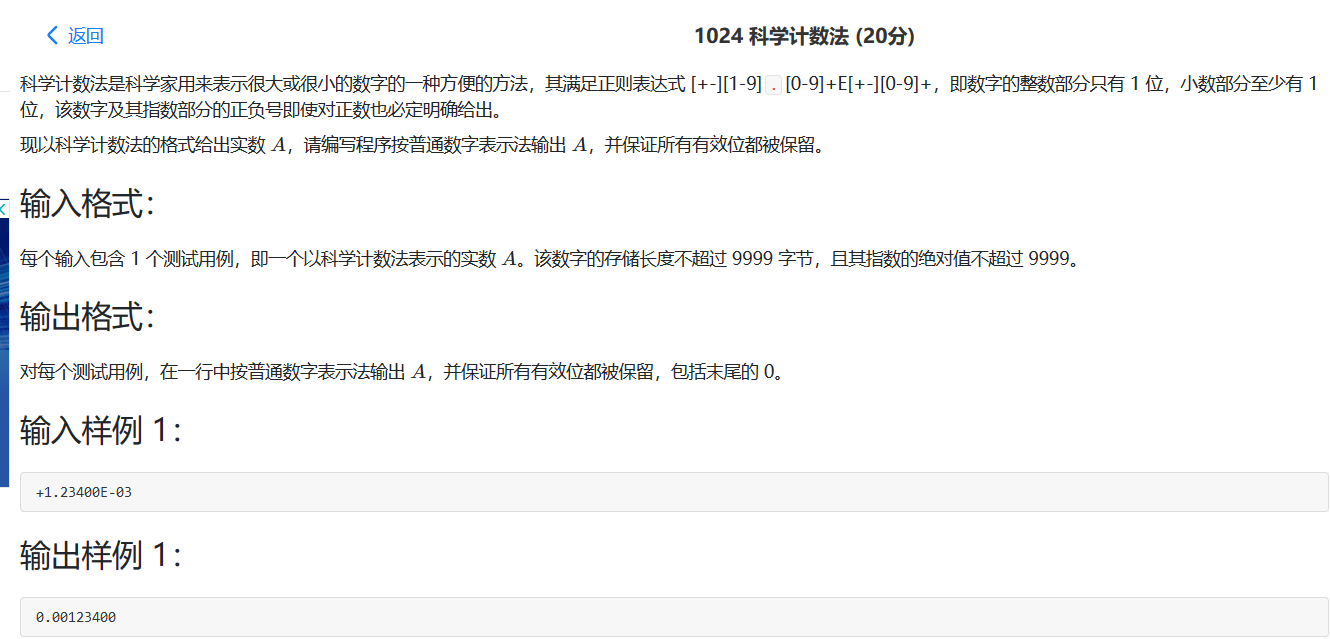
1024 科学计数法 写起来有点小麻烦,还是思维方法不到位的原因。
在指数为正的时候花了些时间,哪里从小数点后有几位数有效数字分情况的话,条理就会清楚很多。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int n = 0 , i = 1 , flag = 0 ; char s[100000 ] = {0 }, ans[100000 ] = {0 }; gets(s); if (s[0 ] == '-' ) flag = 1 ; while (s[i++] != 'E' ); n = atoi(s+i+1 ); if (s[i] == '-' ) { int j = 0 , k = 0 ; if (n) for (j = 0 ; j < n+1 ; j++) ans[j] = j == 1 ? '.' :'0' ; for (k = 1 ; k < i-1 ; k++) if (k != 2 ) ans[j++] = s[k]; } else { if (n < i-4 ) { int j = 0 , k = 1 ; for (k = 1 ; j < n+1 ; k++) if (k != 2 ) ans[j++] = s[k]; ans[j++] = '.' ; for ( ; k < i-1 ; k++) ans[j++] = s[k]; } else { int j = 0 , k = 0 ; for (k = 1 ; k < i-1 ; k++) if (k != 2 ) ans[j++] = s[k]; for (k = 0 ; k < n-(i-4 ); k++) ans[j++] = '0' ; } } if (flag) putchar ('-' ); puts (ans); return 0 ; }
总结:记住 atoi()函数是字符串转化为整数,与另外一个相对的函数总是记混。
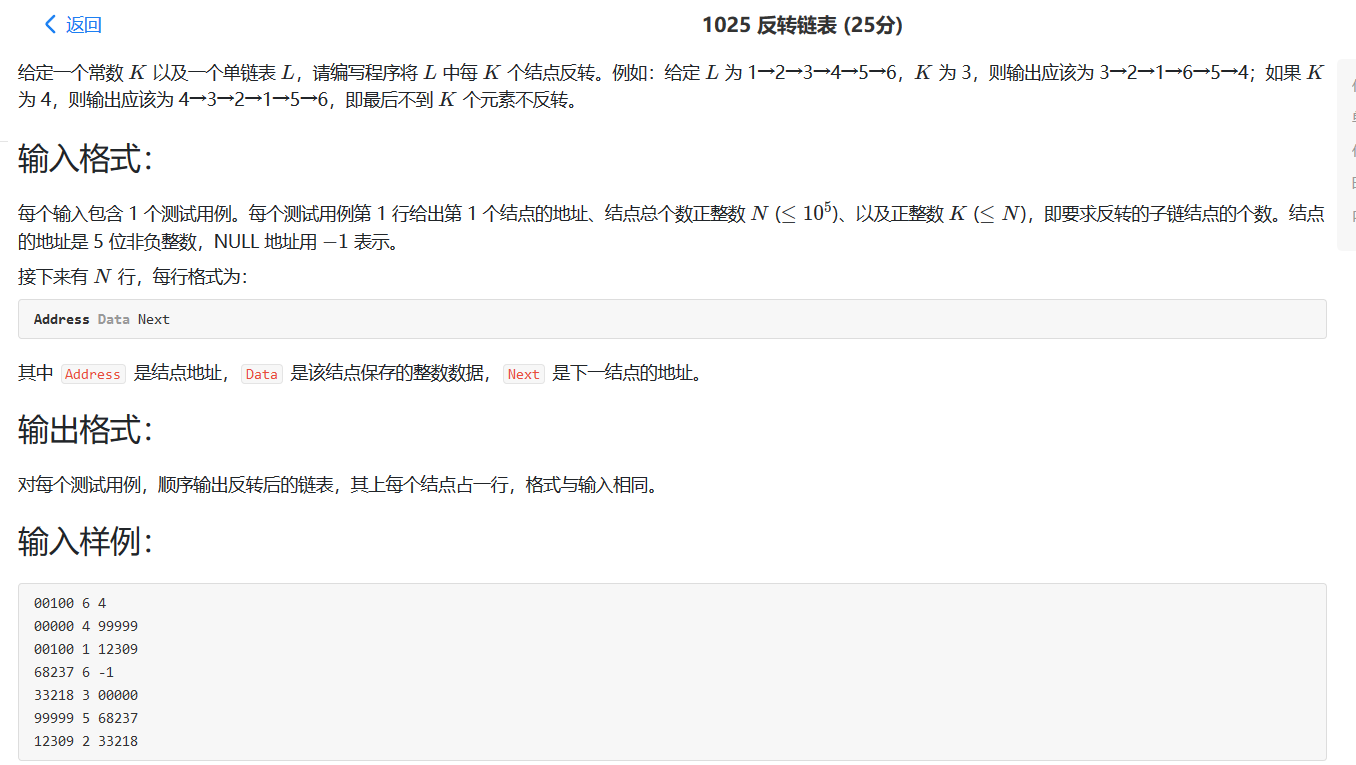
1025 反转链表 发现对于我现在的水平,做乙级的难题还要磨合磨合。
首先用一个结构体代表每个节点的数据,先储存在一个数组。然后根据的节点next关系使用选择排序对节点进行排序,最后反转。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> typedef struct { int addr, data, next; }List; int main (void ) List temp = {0 }; int next = 0 , n = 0 , k = 0 , i = 0 , j = 0 ; scanf ("%d %d %d" , &next, &n, &k); List *list = (List *)malloc (sizeof (List)*n); memset (list , 0 , sizeof (List)*n); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) scanf ("%d %d %d" , &list [i].addr, &list [i].data, &list [i].next); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (j = i; j < n; j++) { if (list [j].addr == next) { temp = list [j]; list [j] = list [i]; list [i] = temp; next = list [i].next; if (next == -1 ) n = i+1 ; break ; } } } for (i = 0 ; i < n; i += k) { int l = i, r = i+k-1 ; if (r >= n) break ; while (l < r) { temp = list [l]; list [l] = list [r]; list [r] = temp; l++, r--; } } for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) if (i == n-1 ) printf ("%05d %d -1\n" , list [i].addr, list [i].data); else printf ("%05d %d %05d\n" , list [i].addr, list [i].data, list [i+1 ].addr); return 0 ; }
总结:难。
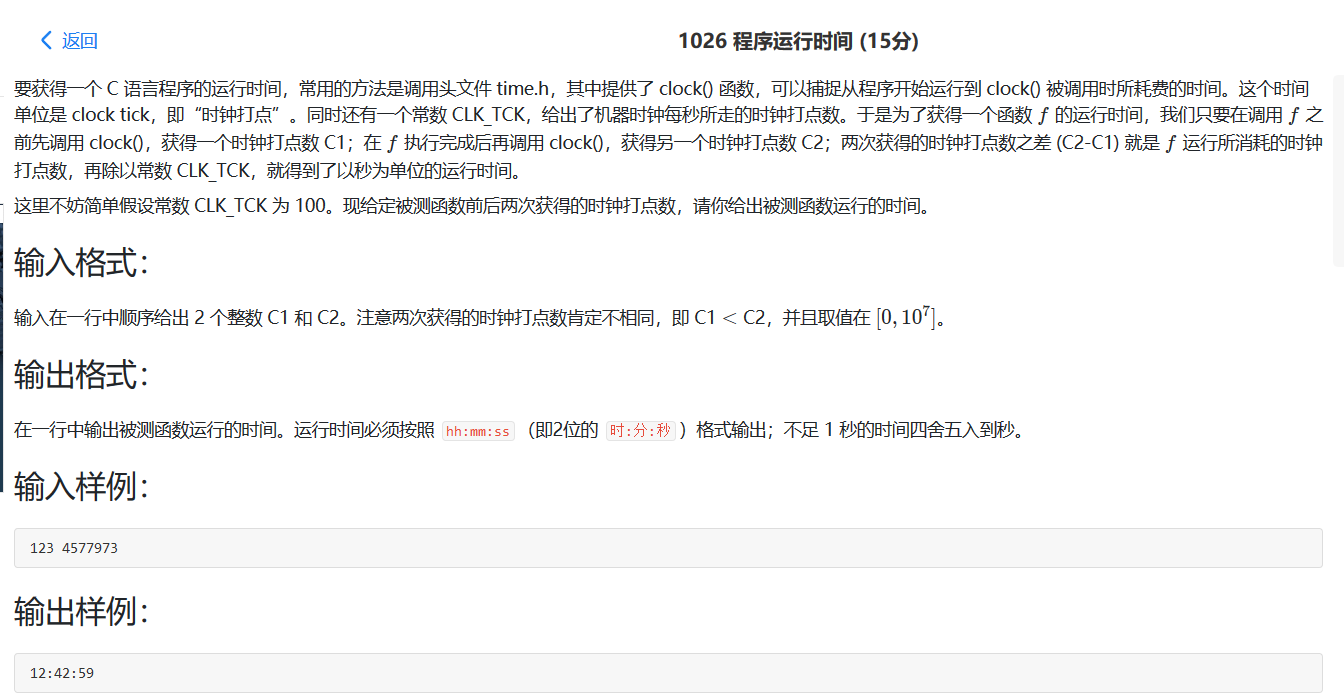
1026 程序运行时间 这个题的条件:不足 1 秒的时间四舍五入到秒。硬是想了好久。🤣
后面发现,其实影响那个精度的在第一次除以CLK_TCK的时候,一个巧妙的办法就是除完后加0.5。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int h = 0 , m = 0 , s = 0 ; int c1 = 0 , c2 = 0 , tck = 100 , ans = 0 ; scanf ("%d %d" , &c1, &c2); ans = (int )((1.0 *(c2-c1)/100 +0.5 )); h = ans/3600 ; m = ans%3600 /60 ; s = ans%3600 %60 ; printf ("%02d:%02d:%02d" , h, m, s); return 0 ; }
1027 打印沙漏 难点:一个高中数学问题,找规律求前等差数列前n项和。打印倒是简单。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) char ch = 0 ; int n = 0 , i = 0 , row = 0 , j = 0 ; scanf ("%d %c" , &n, &ch); for (i = 0 ; ; i++) if (2 *i*(i+2 )+1 > n) { row = i-1 ; break ; } for (i = 0 ; i < row; i++) { for (j = 0 ; j < i; j++) putchar (' ' ); for (j = 0 ; j < (row*2 +1 )-2 *i; j++) putchar (ch); putchar (10 ); } for (i = 0 ; i < row+1 ; i++) { for (j = 0 ; j < row-i; j++) putchar (' ' ); for (j = 0 ; j < 2 *i+1 ; j++) putchar (ch); putchar (10 ); } printf ("%d" , n-(2 *row*(row+2 )+1 )); return 0 ; }
总结:第一次看到,感觉高中知识都忘完了。真的要好好学习大学高等数学。
1028 人口普查 这个题用之前上C语言课老师讲的联合位域来存储日期做很简单,但是还是被题目中的0条件卡了很久,这已经是很多次被PAT乙级的0条件卡了,这个条件真不能大意。
1.开始没有注意,在比较的人里开始不能以0为下标,因为0可能是不合法的人。2.当人数为0时,最后只输出一个0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> typedef union { int data_compare; struct { int day: 5 ; int month: 4 ; int year: 12 ; }; }Date; typedef struct { char name[10 ]; Date date; }People; int main (void ) int max = 0 , min = 0 , i = 0 , flag = 1 ; Date date1 = {0 }, date2 = {0 }; int n = 0 , year = 0 , month = 0 , day = 0 , count = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &n); People *people = (People *)malloc (sizeof (People)*n); memset (people, 0 , sizeof (People)*n); date1.year = 2014 , date1.month = 9 , date1.day = 6 ; date2.year = 1814 , date2.month = 9 , date2.day = 6 ; while (i < n) { scanf ("%s %d/%d/%d" , people[i].name, &year, &month, &day); people[i].date.year = year, people[i].date.month = month, people[i].date.day = day; if (people[i].date.data_compare >= date2.data_compare && people[i].date.data_compare <= date1.data_compare) { if (flag) max = i, min = i, flag = 0 ; count++; if (people[max ].date.data_compare > people[i].date.data_compare) max = i; else if (people[min ].date.data_compare < people[i].date.data_compare) min = i; } i++; } if (count) printf ("%d %s %s" , count, people[max ].name, people[min ].name); else printf ("0" ); return 0 ; }
总结:这个方法比较日期大小真不错。
1030 完美数列
关键在于写循环时注意一个节省时间的技巧。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <stdio.h> int cmp (const void *a, const void *b) return *(int *)a - *(int *)b; } int main (void ) double p = 0 ; int n = 0 , a[100000 ], i = 0 , j = 0 , max = 1 ; scanf ("%d %lf" , &n, &p); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) scanf ("%d" , a+i); qsort(a, n, sizeof (int ), cmp); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (j = i+max ; j < n; j++) { if (a[j] > a[i]*p) { max = j-i > max ? j-i : max ; break ; } else if (j == n-1 ) { max = j-i+1 > max ? j-i+1 : max ; break ; } } } printf ("%d" , max ); return 0 ; }
总结:遍历时注意能不能节省时间。
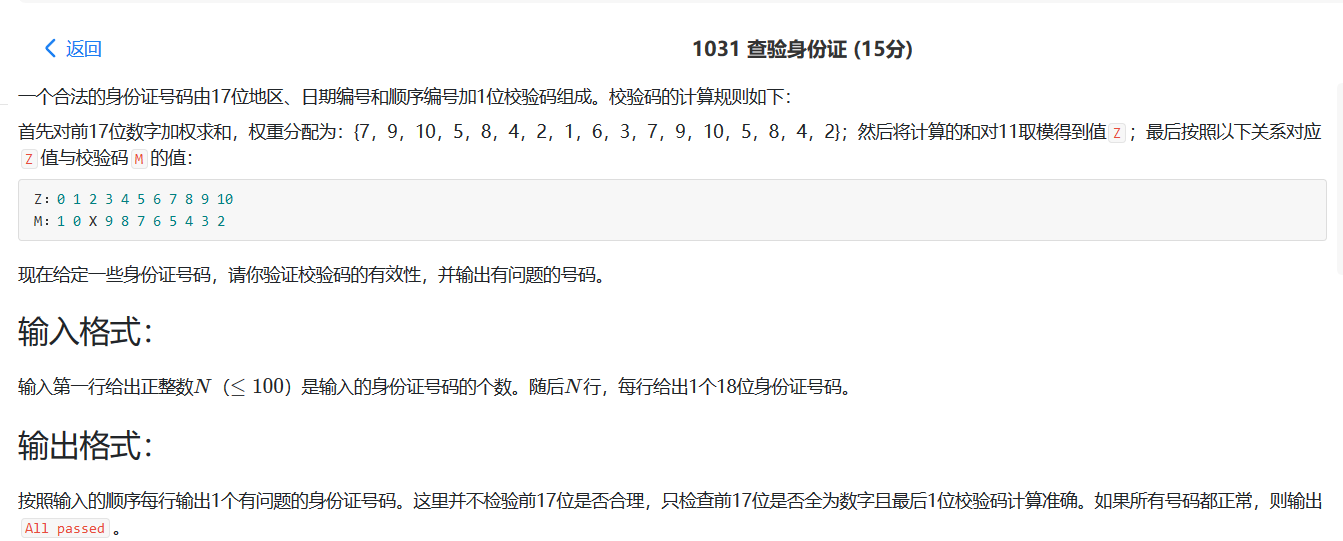
1031 查验身份证 这道题看出,我对权重有误解。。。开始都去乘个0.01。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int n = 0 , i = 0 , flag = 0 , sum = 0 ; char a[] = {'1' , '0' , 'X' , '9' , '8' , '7' , '6' , '5' , '4' , '3' , '2' }; int q[17 ] = {7 , 9 , 10 , 5 , 8 , 4 , 2 , 1 , 6 , 3 , 7 , 9 , 10 , 5 , 8 , 4 , 2 }; char s[19 ] = {0 }; scanf ("%d" , &n); getchar(); while (n--) { gets(s); for (i = 0 , sum = 0 ; i < 17 ; i++) sum += (s[i]-48 )*q[i]; sum = sum%11 ; if (a[sum] != s[17 ]) printf ("%s\n" , s), flag = 1 ; } if (!flag) printf ("All passed\n" ); return 0 ; }
总结:权重。。
1033 旧键盘打字 关键是统计坏掉的键时注意一个字母坏了,与之对应的大写或小写都要置坏的标志位。这个还要开始就写,不然后面很麻烦。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int a[127 ] = {0 }, i = 0 ; char s[100001 ] = {0 }, ch = 0 ; while ((ch = getchar()) != 10 ) { if (ch >= 65 && ch <= 90 ) a[ch]++, a[ch+32 ]++; else if (ch >= 97 && ch <= 122 ) a[ch]++, a[ch-32 ]++; else a[ch]++; } gets(s); for (i = 0 ; s[i]; i++) { if (a['+' ]) { if (a[s[i]] == 0 && (s[i] < 65 || s[i] > 90 )) printf ("%c" , s[i]); } else { if (a[s[i]] == 0 ) printf ("%c" , s[i]); } } return 0 ; }
总结:无。
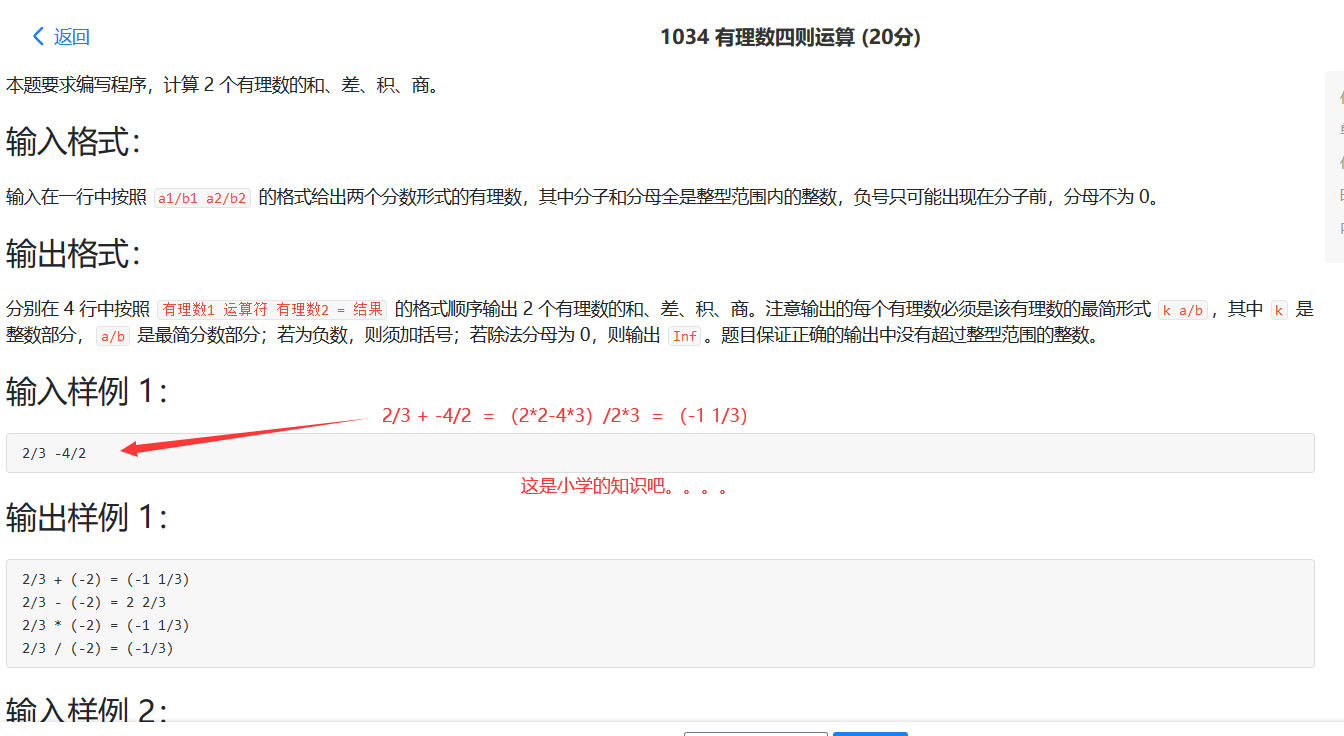
1034 有理数四则运算 我居然一直不知道分数的加减法可以直接写的,还在哪里通分后计算。。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #include <stdio.h> void gcd (long a, long b) if (b == 0 ) { printf ("Inf" ); return ; } long a1 = a, b1 = b, c = 0 , flag = 1 ; if (a1 < 0 ) a1 *= -1 , a *= -1 , flag *= -1 ; if (b1 < 0 ) b1 *= -1 , b *= -1 , flag *= -1 ; if (a) { while (b1) { c = a1%b1; a1 = b1; b1 = c; } a /= a1, b /= a1; } if (flag < 0 ) printf ("(-" ); if (a/b && a%b) printf ("%ld %ld/%ld" , a/b, a%b, b); else if (a%b) printf ("%ld/%ld" , a%b, b); else printf ("%ld" , a/b); if (flag < 0 ) printf (")" ); } int main (void ) char op[5 ] = "+-*/" , i = 0 ; long a1 = 0 , a2 = 0 , b1 = 0 , b2 = 0 ; scanf ("%ld/%ld %ld/%ld" , &a1, &a2, &b1, &b2); for (i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { gcd(a1, a2); printf (" %c " , op[i]); gcd(b1, b2); printf (" = " ); switch (op[i]) { case '+' : gcd(a1*b2+a2*b1, a2*b2);break ; case '-' : gcd(a1*b2-a2*b1, a2*b2);break ; case '*' : gcd(a1*b1, a2*b2);break ; case '/' : gcd(a1*b2, a2*b1);break ; } putchar (10 ); } return 0 ; }
总结:分数加减法与输出格式的学习。
1035 插入与归并 关键在于了解插入与归并排序的原理,然后使用qsort来模拟两种排序算法 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <stdio.h> int cmp (const void *a, const void *b) return *(int *)a - *(int *)b; } int main (void ) int i = 0 , j = 0 , flag = 1 , k = 1 ; int n = 0 , a[100 ] = {0 }, b[100 ] = {0 }; scanf ("%d" , &n); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) scanf ("%d" , a+i); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) scanf ("%d" , b+i); for (i = 0 ; i < n-1 && b[i] <= b[i+1 ]; i++); for (j = i+1 ; a[j] == b[j] && j < n; j++); if (j == n) { puts ("Insertion Sort" ); qsort(a, i+2 , sizeof (int ), cmp); } else { puts ("Merge Sort" ); while (flag) { k *= 2 ; flag = 0 ; for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) if (a[i] != b[i]) flag = 1 ; for (i = 0 ; i < n/k; i++) qsort(a+k*i, k, sizeof (int ), cmp); qsort(a+n/k*k, n-(n/k*k), sizeof (int ), cmp); } } printf ("%d" , a[0 ]); for (i = 1 ; i < n; i++) printf (" %d" , a[i]); return 0 ; }
总结:排序算法的了解与qsort的运用。
1040 有几个PAT 做这个的题的思路真是秒啊,果然好想的方法写起来多,不容易想到的方法代码量又少效率又高。
先统计所有’T’的个数,再依次遍历。如果在前面遇到的’P’则P的个数加1,遇到’T’则T的个数减一,遇到’A’则总个数直接加上此时P的个数与T的个数乘积。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) char s[100001 ] = {0 }; long ans = 0 , count_t = 0 , count_p = 0 , i = 0 ; gets(s); for (i = 0 ; s[i]; i++) if (s[i] == 'T' ) count_t ++; for (i = 0 ; s[i]; i++) { if (s[i] == 'P' ) count_p++; else if (s[i] == 'T' ) count_t --; else ans += count_p*count_t ; } printf ("%d" , ans%1000000007 ); return 0 ; }
1041 考试座位号 从这道题找出了以前不清楚的知识点。
scanf();后如果是是用gets()输入字符串,那必须先吃掉回车;如果是用scanf(“%s”, );输入字符串可以不吃掉回车。
成功跳进上图标出的坑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> typedef struct { char id[17 ]; int z2; }People; int main (void ) char id_[17 ] = {0 }; int n = 0 , z1_ = 0 , z2_ = 0 , temp = 0 ; People people[1001 ] = {0 }; scanf ("%d" , &n); while (n--) { scanf ("%s %d %d" , id_, &z1_, &z2_); strcpy (people[z1_].id, id_); people[z1_].z2 = z2_; } scanf ("%d" , &n); while (n--) { scanf ("%d" , &temp); printf ("%s %d\n" , people[temp].id, people[temp].z2); } return 0 ; }
1045 快速排序
这个题关键在于一个点:只要某个元素的位置没有变,我们只要保证左边的元素最大值都比它小,那该元素左边的元素都比它小,右边的元素都比它大。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <stdio.h> int cmp (const void *a, const void *b) return *(int *)a - *(int *)b; } int main (void ) int N = 0 , i = 0 , count = 0 , max = 0 ; int p[100001 ], p1[100001 ], p2[100001 ]; scanf ("%d" , &N); for (i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { scanf ("%d" , &p[i]); p1[i] = p[i]; } qsort(p, N, sizeof (int ), cmp); for (i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { if (p[i] == p1[i] && p1[i] > max ) p2[count++] = p[i]; if (p1[i] > max ) max = p1[i]; } printf ("%d\n" , count); if (count) printf ("%d" , p2[0 ]); for (i = 1 ; i < count; i++) printf (" %d" , p2[i]); putchar (10 ); return 0 ; }
1048 数字加密 题目不难又是坑人的隐含条件。。
这里说2个整数每一位对应数字进行运算,但有个情况就是B的长度小于A的长度的时候就要在B的前面用’0’补齐与A一样的长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main (void ) int l_a = 0 , l_b = 0 , i = 0 ; char a[201 ] = {0 }, b[201 ] = {0 }, c[201 ] = {0 }; char s[14 ] = "0123456789JQK" ; scanf ("%s %s" , a, b); l_a = strlen (a), l_b = strlen (b); if (l_b < l_a) { while (i < l_a-l_b) c[i++] = '0' ; strcat (c, b); strcpy (b, c); } i = 1 , l_b = strlen (b); while (i <= l_a) { if (i%2 ) b[l_b-i] = s[(b[l_b-i]-48 +a[l_a-i]-48 )%13 ]; else { int temp = (b[l_b-i]-48 )-(a[l_a-i]-48 ); b[l_b-i] = temp < 0 ? temp+10 +48 :temp+48 ; } i++; } puts (b); return 0 ; }
1049 数列的片段和 不会动态规划,算法没有学习过,做这个题看了柳神的算法,厉害。。。
算法:算出每个数一共会在片段中出现的次数,然后相乘。最后所有数据相加即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int n = 0 , i =1 ; double temp = 0 ; long long ans = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &n); for (i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { scanf ("%lf" , &temp); ans += (long long )(temp*1000 )*i*(n-i+1 ); } printf ("%.2lf" , ans/1000.0 ); return 0 ; }
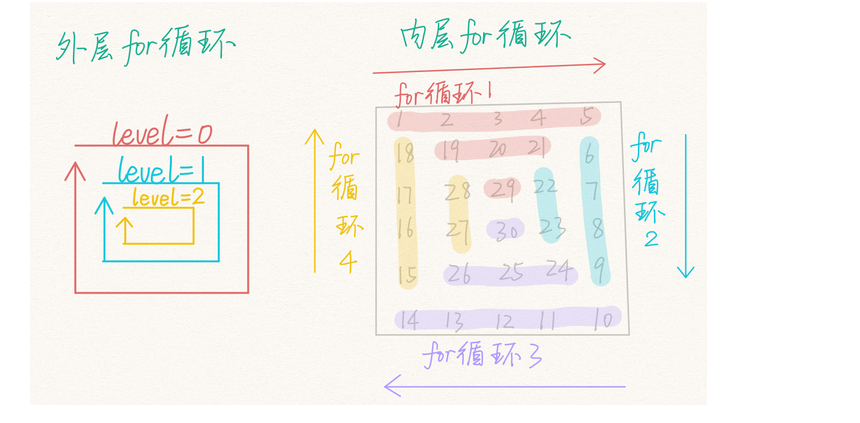
1050 螺旋矩阵
开始想的是从外层一圈一圈的填充,但是最后也只能填充最外层,内层填充不好插进去。。。
下面是柳婼 の blog 的填充方法给出的图:真的清晰明了。其实这也是最基本应该想到的常规方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <stdlib.h> int a[100000 ] = {0 };int ans[100000 ] = {0 };int cmp (const void *a, const void *b) return *(int *)b - *(int *)a; } void filling (int *ans, int *a, int m, int n, int N) int i = 0 , j = 0 , level = m/2 +m%2 , t = 0 ; for (i = 0 ; i < level; i++) { for (j = i; j <= n-1 -i && t <= N-1 ; j++) ans[i*n+j] = a[t++]; for (j = i+1 ; j <= m-2 -i && t <= N-1 ; j++) ans[j*n+n-1 -i] = a[t++]; for (j = n-1 -i; j >= i && t <= N-1 ; j--) ans[(m-1 -i)*n+j] = a[t++]; for (j = m-2 -i; j >= i+1 && t <= N-1 ; j--) ans[j*n+i] = a[t++]; } } int main (void ) int i = 0 , j = 0 ; int N = 0 , m = 0 , n = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &N); n = (int )sqrt (N); while (n) { if (N%n == 0 ) { m = N/n; break ; } n--; } for (i = 0 ; i < N; i++) scanf ("%d" , a+i); qsort(a, N, sizeof (int ), cmp); filling(ans, a, m, n, N); for (i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { printf ("%d" , ans[i*n+j]); if (j != n-1 ) putchar (32 ); } putchar (10 ); } return 0 ; }
1051 复数乘法
为什么PAT的题有这么多坑。。首先这里的给的辐角已经是弧度制了,所以不用转换;其次就是结果保留2位小数,那当结果小于0但大于-0.01时,比如-0.001,这时候保留2位小数就只有0,所以最后输出的时候也不应该有负号。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int main (void ) double r1 = 0 , p1 = 0 , r2 = 0 , p2 = 0 ; double a1 = 0 , b1 = 0 , a2 = 0 , b2 = 0 ; double ans1 = 0 , ans2 = 0 ; scanf ("%lf %lf %lf %lf" , &r1, &p1, &r2, &p2); a1 = r1*cos (p1); b1 = r1*sin (p1); a2 = r2*cos (p2); b2 = r2*sin (p2); ans1 = a1*a2+(-1 )*b1*b2; ans2 = a1*b2+a2*b1; if (ans1 < 0 && ans1 > -0.01 ) ans1 = 0 ; if (ans2 < 0 && ans2 > -0.01 ) ans2 = 0 ; printf ("%.2lf" , ans1); if (ans2 >= 0 ) putchar ('+' ); printf ("%.2lfi" , ans2); return 0 ; }
1052 卖个萌 考点:字符串的分割,使用一个指针数组来存储地址。
写完,在本地C语言环境发现VC与DEVC一得不到正确的结果,调式才发现这2个环境都不能识别输入的表情符号,然后都以0来填充。这也是本题我的难点,找错半天。。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <stdio.h> void fun (char *a[], char *s) int i = 0 , j = 0 ; while (s[i]) { if (s[i] == '[' ) a[j++] = s+i+1 ; else if (s[i] == ']' ) s[i] = '\0' ; i++; } } int main (void ) int n = 0 , i = 0 ; char *a[3 ][100 ] = {NULL }, s[3 ][100 ] = {0 }; int zs, zy, k, yy, ys; for (i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { gets(s[i]); fun(a[i], s[i]); } scanf ("%d" , &n); while (n--) { scanf ("%d %d %d %d %d" , &zs, &zy, &k, &yy, &ys); if (!a[0 ][zs-1 ] || !a[0 ][ys--] || !a[1 ][zy-1 ] || !a[1 ][yy-1 ] || !a[2 ][k]) printf ("Are you kidding me? @\\/@\n" ); else printf ("%s%s%s%s%s" , a[0 ][zs-1 ], a[1 ][zy-1 ], a[2 ][k], a[1 ][yy-1 ], a[0 ][ys-1 ]); } return 0 ; }
最后:还有一个注意的地方就是,使用指针数组存放一个数组的指针字符串的地址后,该数组不能改变啊。大意就容易出错。
1054 求平均值 这个题开始自己了判断是否是合法数据的函数,但一只有一个测试点过不了,就开始找判断函数的问题,果然有问题,但修改后仍然有测试点过不了。
原来因为题不中的一句话:如果 K 为 1,则输出 The average of 1 number is Y,这里的number是单数。。。
另外就是这个题,直接用sscanf与sprintf对数据进行相互转换,如果不相等则不合法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main (void ) char s[1000 ] = {0 }, t[1000 ] = {0 }; int n = 0 , count = 0 , i = 0 , flag = 0 ; double sum = 0 , temp = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &n); while (n--) { scanf ("%s" , s); sscanf (s, "%lf" , &temp); sprintf (t, "%.2lf" , temp); for (i = 0 ; i < strlen (s); i++) if (s[i] != t[i]) flag = 1 ; if (!flag && temp >= -1000 && temp <= 1000 ) sum += temp, count++; else printf ("ERROR: %s is not a legal number\n" , s); strcpy (s, "" ), flag = 0 ; } if (count == 1 ) printf ("The average of 1 number is %.2lf" , sum/count); else if (count) printf ("The average of %d numbers is %.2lf" , count, sum/count); else printf ("The average of 0 numbers is Undefined" ); return 0 ; }
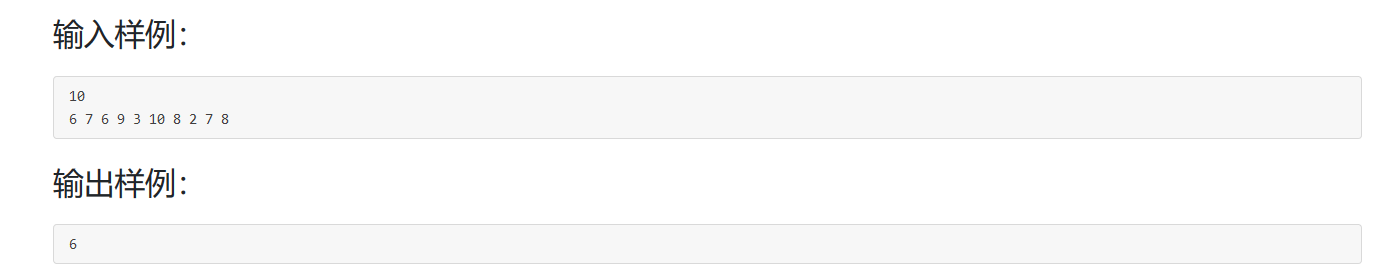
1060 爱丁顿数
难在题目意思开始没有理解。其实就是让我们找到给定骑车天数中,E天骑车超过E英里的最大E。如给定的例子,在给定10天骑车中,有6天骑车都超过6英里。且这个6是能找到最大的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <stdio.h> int cmp (const void *a, const void *b) return *(int *)a > *(int *)b ? -1 :1 ; } int main (void ) int n = 0 , i = 1 , a[100001 ], ans = 0 , p = 1 ; scanf ("%d" , &n); for (i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) scanf ("%d" , a+i); qsort(a+1 , n, sizeof (int ), cmp); while (ans <= n && a[p] > p) ans++, p++; printf ("%d" , ans); return 0 ; }
1062 最简分数
就是上面的一个坑点。。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include <stdio.h> int gcd (int a, int b) return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b); } void swap (double *a, double *b) double temp = *a; *a = *b; *b = temp; } int main (void ) int i = 0 , count = 0 , k = 0 ; double a, a1, b, b1; scanf ("%lf/%lf %lf/%lf %d" , &a, &a1, &b, &b1, &k); a *= k/a1, b *= k/b1; if (a > b) swap(&a, &b); b = b>(int )b ? b+1 :b; for (i = (int )a+1 ; i < (int )b; i++) if (gcd(i, k) == 1 ) if (count == 0 ) printf ("%d/%d" , i, k), count = 1 ; else printf (" %d/%d" , i, k); return 0 ; }
1065 单身狗 真的吐了,又是被PAT乙级输出格式找了半天错。
另外就是,还是0作怪。。我用0做存放夫妻数组的初始化,让夫妻达到相互映射关系,但是忘了有夫妻的id是0啊。。。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <stdio.h> int main (void ) int n = 0 , count = 0 , i = 0 ; int a[100000 ], b[100000 ] = {0 }; scanf ("%d" , &n); for (i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) a[i] = -1 ; while (n--) { int id1, id2; scanf ("%d %d" , &id1, &id2); a[id1] = id2, a[id2] = id1; } scanf ("%d" , &n); while (n--) { int id; scanf ("%d" , &id); b[id]++; } for (i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) if (b[i] && (a[i] < 0 || !b[a[i]])) count++, b[i] = -1 ; printf ("%d\n" , count); for (i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) if (b[i] == -1 && count > 1 ) printf ("%05d " , i), count--; else if (b[i] == -1 ) printf ("%05d" , i); return 0 ; }